how to enable afib monitoring on fitbit and why you should

Fitbit’s smartwatches and fitness trackers feature accurate heart rate monitors that provide valuable insight into our heart’s rhythm when resting or on the go. However, heart rate alone is only a tiny snapshot of our overall heart health. Fitbit recently announced plans to include atrial fibrillation (AFib) notifications and irregular heart rhythm monitoring in a select number of its devices. In this article, we will discuss what is AFib, why is it important, and how can you use your Fitbit device to monitor for instances of it.
What is AFib?
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) occurs when the heart’s upper sections beat at different rhythms, resulting in a quickened, irregular heart rate. According to Mayo Clinic, this condition could also result in shortness of breath, poor blood flow, and blood clots in the heart. AFib also increases the risk of a stroke. For this reason, it’s important that users susceptible to AFib use a heart rate monitor that can detect these abnormalities. Fitbit’s AFib feature is a great safety tool.
How does Fitbit monitor AFib?
Fitbit devices don’t have any dedicated AFib sensors onboard. Instead, they use their heart rate (PPG) sensors to keep track of your pulse rhythm. Viable data is collected over time and analyzed to provide a baseline heart rhythm. Fitbit can then compare this baseline to beat-by-beat measurements, and alert users if it notices a large enough discrepancy. For context, Fitbit suggests a 10bpm increase in a short period of time might be enough to be considered irregular, but this data will vary from person to person.
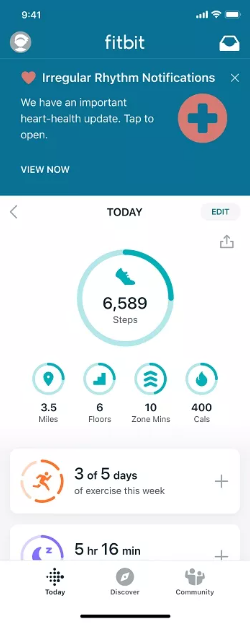
How to Enable Afib Monitoring on Fitbit and Why You Should?
To enable Afib monitoring on a Fitbit device, you will need a device that supports the feature, such as the Fitbit Sense or Fitbit Versa 3. Once you have a device that supports Afib monitoring, you can enable the feature by following these steps:
- Open the Fitbit app on your smartphone
- Tap on the Today tab, then tap on the device icon
- Scroll down to the Health Features section, and tap on the ECG app
- Follow the on-screen instructions to set up the ECG app and enable Afib monitoring
It is important to note that Afib monitoring is not intended to replace a visit to a healthcare professional and should not be used to diagnose or treat a medical condition. However, it can be a useful tool for tracking your heart health and identifying potential issues that may require further evaluation.
Afib monitoring can help detect irregular heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation, which can lead to stroke and other serious health complications if left untreated. It can also provide valuable information to your healthcare provider when monitoring and managing your heart health.
What about Fitbit’s ECG feature?
While the two features focus on monitoring heart rate health, the processes are entirely different. The ECG (electrocardiogram) sensors on the Fitbit Charge 5, Fitbit Sense, and Sense 2 use electrical signals to survey a user’s heart performance in 30-second bites. To get an ECG reading, users need to initiate the process, and the resultant data is presented in a detailed PDF. A doctor can use the data acquired by the ECG to detect AFib, but as it’s a spot check, you won’t get any automated notifications if an instance is detected.
Fitbit devices that support AFib monitoring
Fitbit announced plans to introduce irregular heart rhythm monitoring smarts in April 2022 to many legacy devices. Impressively, it’s not just the company’s latest smartwatches and trackers that gain the feature.
Conclusion
Fitbit’s AFib monitoring feature is a great addition to its heart rate monitoring capabilities. It can detect possible instances of AFib and notify users, which can help users take the necessary steps to maintain their heart health. Additionally, Fitbit has made the feature available on many legacy devices, making it accessible to a wide range of users. It is important to note that the feature is not a substitute for professional medical advice, but it can be used as an additional tool to monitor and maintain heart health.
For more information check out the original article at Fibit.com